Running and Quitting
Overview
Teaching: 15 min
Exercises: 0 minQuestions
How can I run Python programs?
Objectives
Launch the Jupyter Notebook, create new notebooks, and exit the Notebook.
Create Markdown cells in a notebook.
Create and run Python cells in a notebook.
Getting the Data
The data we will be using is taken from the [gapminder][gapminder] dataset. Create a directory called
python-novice-gapminder, and download the zip file python-novice-gapminder-data.zip into it. Then unzip the file (it should create adatafolder. Then start a Jupyter notebook from inside this directory (see the second header below).
Python programs are plain text files.
- They have the
.pyextension to let everyone (including the operating system) know it is a Python program.- This is convention, not a requirement.
- It’s common to write them using a text editor but we are going to use the Jupyter Notebook.
- The bit of extra setup is well worth it because the Notebook provides code completion and other helpful features.
- Notebook files have the extension
.ipynbto distinguish them from plain-text Python programs.- Can export as “pure Python” to run from the command line.
Use the Jupyter Notebook for editing and running Python.
- The Anaconda package manager is an automated way to install the Jupyter notebook.
- See the setup instructions for Anaconda installation instructions.
- It also installs all the extra libraries it needs to run.
-
Once you have installed Python and the Jupyter Notebook requirements, open a shell and type:
$ jupyter notebook - This will start a Jupyter Notebook server and open your default web browser.
- The server runs locally on your machine only and does not use an internet connection.
- The server sends messages to your browser.
- The server does the work and the web browser renders the notebook.
- You can type code into the browser and see the result when the web page talks to the server.
- This has several advantages:
- You can easily type, edit, and copy and paste blocks of code.
- Tab complete allows you to easily access the names of things you are using and learn more about them.
- It allows you to annotate your code with links, different sized text, bullets, etc. to make it more accessible to you and your collaborators.
- It allows you to display figures next to the code that produces them to tell a complete story of the analysis.
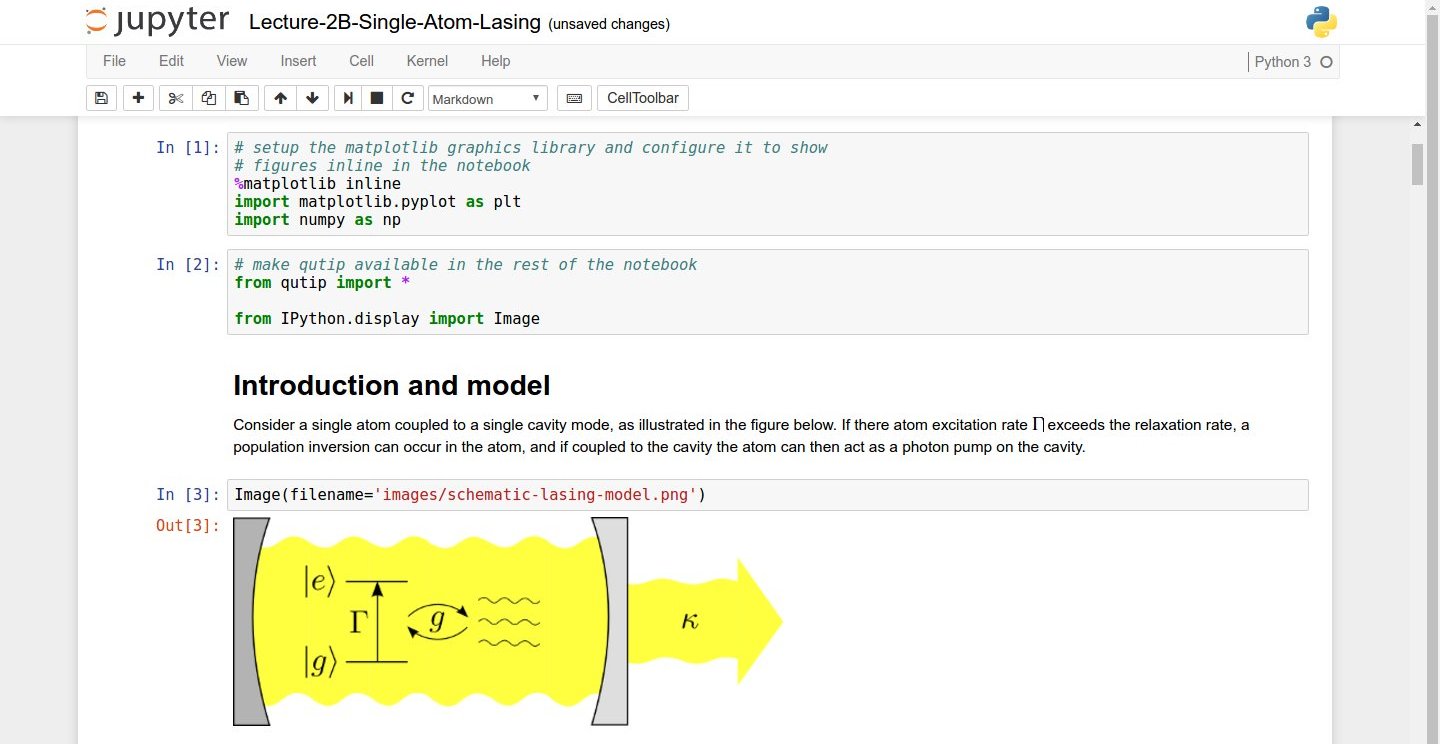
Screenshot of a Jupyter Notebook on quantum mechanics by Robert Johansson
How It’s Stored
- The notebook file is stored in a format called JSON.
- Just like a webpage, what’s saved looks different from what you see in your browser.
- But this format allows Jupyter to mix software (in several languages) with documentation and graphics, all in one file.
Use the keyboard and mouse to select and edit cells.
- Pressing the “return” key turns the border green and engages edit mode, which allows you to type within the cell.
- Because we want to be able to write many lines of code in a single cell, pressing the “return” key when in edit mode (green) moves the cursor to the next line in the cell just like in a text editor.
- We need some other way to tell the Notebook we want to run what’s in the cell.
- Pressing the “shift” and the “enter” key together will execute the contents of the cell.
- Notice that the “return” and “shift” keys on the right of the keyboard are right next to each other.
Use comments to add documentation to programs.
# This sentence isn't executed by Python.
adjustment = 0.5 # Neither is this - anything after '#' is ignored.
More Math
What is displayed when a Python cell in a notebook that contains several calculations is executed? For example, what happens when this cell is executed?
7 * 3 2 + 1Solution
Python returns the output of the last calculation.
3
Key Points
Python programs are plain text files.
Use the Jupyter Notebook for editing and running Python.
The Notebook has Command and Edit modes.
Use the keyboard and mouse to select and edit cells.
The Notebook will turn Markdown into pretty-printed documentation.
Markdown does most of what HTML does.